Scenario description
A domestic self-invoice is a type of invoice when a customer who buys goods or services issues an invoice with chargeable VAT amount.
According to art. 17 c. 2 DPR 633/72, the invoice that an Italian company receives from a non–European Union (EU) vendor doesn’t include any tax amount. The Italian company must calculate the tax amount and use the reverse charge mechanism so that the VAT accounting reflects the tax amount. In this case, the Italian company must issue a domestic self-invoice (autofattura) by the fifteenth day of the next month after the operation date. The autofattura is a mechanism that lets the customer fulfill VAT obligations that are related to the original invoice. The original invoice should be reported together with the calculated VAT amount in both the “Vendite” section and the “Acquisti” section of the sales tax book.
A domestic self-invoice must be issued for the domestic supply of goods and generic services by non-EU vendors to business-to-business (B2B) customers that are established in Italy in accordance with art. 17(2) of the Italian VAT Act.
The accounting obligations must be distinguished from the VAT obligations.
- From an accounting perspective, both the domestic self-invoice that is issued and the non-EU invoice that is received should be posted in the general ledger.
- From a VAT perspective, only the domestic self-invoice must be included in both purchase VAT ledgers and sales VAT ledgers.
In other words, an Italian company that receives an invoice from a non-EU vendor for the domestic supply of goods and generic services must complete these tasks:
- Post the ledger that is received in the general ledger, to show the expense and the debt with the supplier. This invoice should not be posted in the VAT ledgers.
- Issue the domestic self-invoice (additional invoice), and post it in the general ledger, to show the VAT debit and the VAT credit.
- Post the domestic self-invoice invoice from step 2 in both purchase and sales and VAT ledgers. This invoice is posted together with the registration data of the non-EU supplier. A separate number sequence is used to generate a number for this invoice.
The VAT obligations that are related to the transaction can’t be fulfilled by using the original invoice. Therefore, the purpose of the domestic self-invoice is to enable compliance with those VAT obligations.
The Purchases and Sales Invoices Communication report must reflect the VAT amount that was calculated and posted for the purchase in the domestic-self-invoice communication details as following:
|
Schema block of fields
|
Reporting information
|
|
<IdentificativiFiscali> block of fields in the <CedentePrestatoreDTR> block of fields
|
Information about the original vendor (extra-EU vendor)
|
|
<DatiFatturaBodyDTR> block of fields
|
Information from the domestic self-invoice
|
|
<Natura> tag
|
“N6”
|
Functional solution
To meet requirements of specific way of reporting domestic self-invoices in Purchases and Sales Invoices Communication report in Microsoft Dynamics AX the following extensions are done:
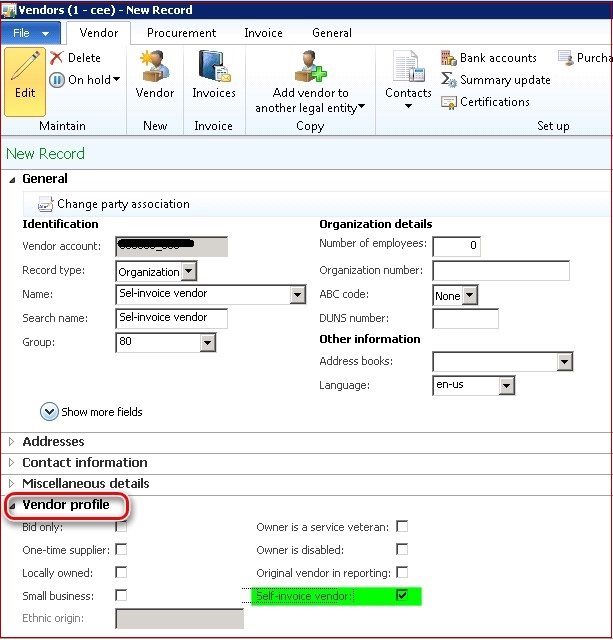
- Vendor master data is extended with the Self-invoice vendor parameter.
- Invoices communication register is extended with the Original vendor field.
On running Add records function in Invoices communication register for self-invoice (with Self-invoice vendor parameter marked on Vendor master data) system will try to find a vendor related by Tax exempt number in the invoice and fill in value of Original vendor field with the Vendor account found. It is also possible to fulfill or update the value manually.
On generation of Purchase invoices communication report if Original vendor field value is not empty then system will print:
- <IdentificativiFiscali> from Original vendor (ISO code related to the Tax exempt number)
- <AltriDatiIdentificativi> from Original vendor primary address.
- <Natura> tag value will be printed with "N6" value.
User guidance
Self-invoice vendor setup
To let system to identify vendor invoices registered as self-invoice, mark Self-invoice vendor parameter of this vendor:
Self-invoice registration
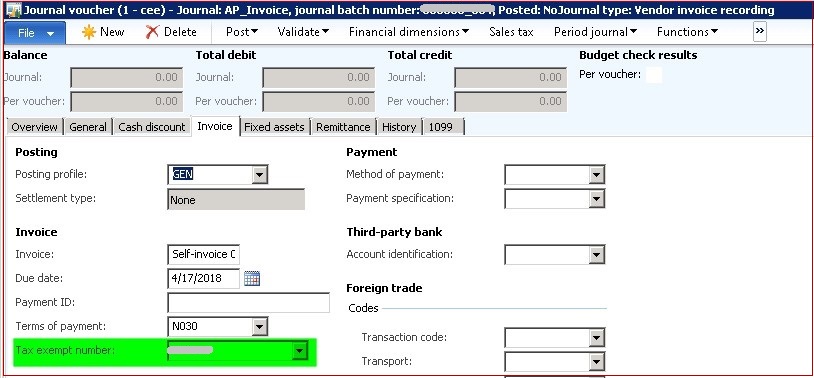
Self-invoice should be registered with Tax exempt number of the original extra-EU vendor. No matter how the self-invoice is created (Vendor invoice, General Journal, Purchase order, Customs declarations), Tax exempt number field value should be filled in with the original extra-EU vendor. As for example, in Vendor invoice:
Invoices communication register
Open General ledger > Reports > External > Invoices communication register and click on Add records button. On adding records to the register, system will identify self-invoices by “Self-invoice vendor” parameter in invoice vendor master data and will try to find an original extra-EU vendor with the same Tax exempt number as in the invoice. If related vendor will be found, it’s account number will be filled in Original vendor field of the invoice. It the system will not be able to find an original extra-EU vendor a warning will be thrown and Original vendor field of the invoice will remain empty. User will be able to fulfill or update the Original vendor field value of the invoice manually if needed.
It is supposed that invoices unnecessary for reporting can be filtered out via customization of the query on Add records function, or Invoices communication setup, or customization of the query on Export (Re-export) function.